Nyzo Micropay for Android version 1 (commit on GitHub) introduces the Micropay app with payment functionality.
This is a new code base that borrows heavily from the Nyzo Java verifier source. Where appropriate, equivalent classes in this and the Nyzo verifier source will be kept as similar as possible.
Prior to this version, only resource files (mostly icons), build files, and Git ignore files were committed to the repository. This is the first commit that contains Java source code.
If you are unfamiliar with Android development, this project is likely not a good introduction to the topic. It is unorthodox in its treatment of the view hierarchy and its avoidance of XML files in favor of Java source. If you are familiar with Android development, we hope this provides an amusing new perspective to you.
The manifest is a typical Android manifest file. This is where the version is specified. The nyzo://micropay URL scheme is specified, and this is how requests for payment are passed to the Micropay app. The the Micropay image example page already contains a usage of this URL scheme.

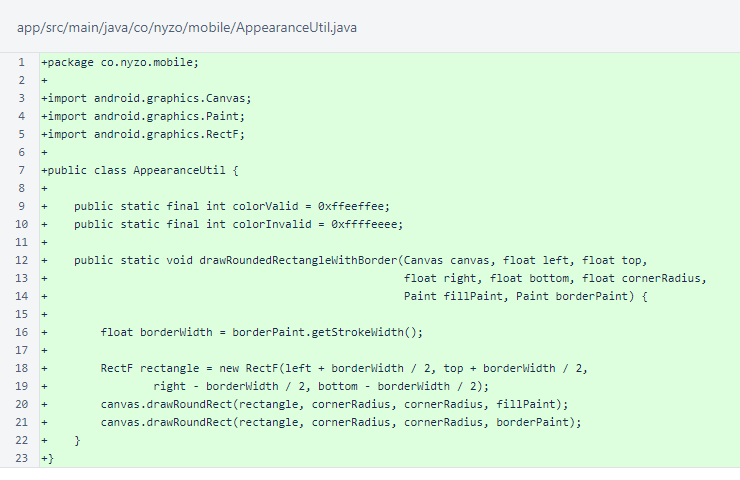
The AppearanceUtil class contains some colors and a method to assist in interface rendering.
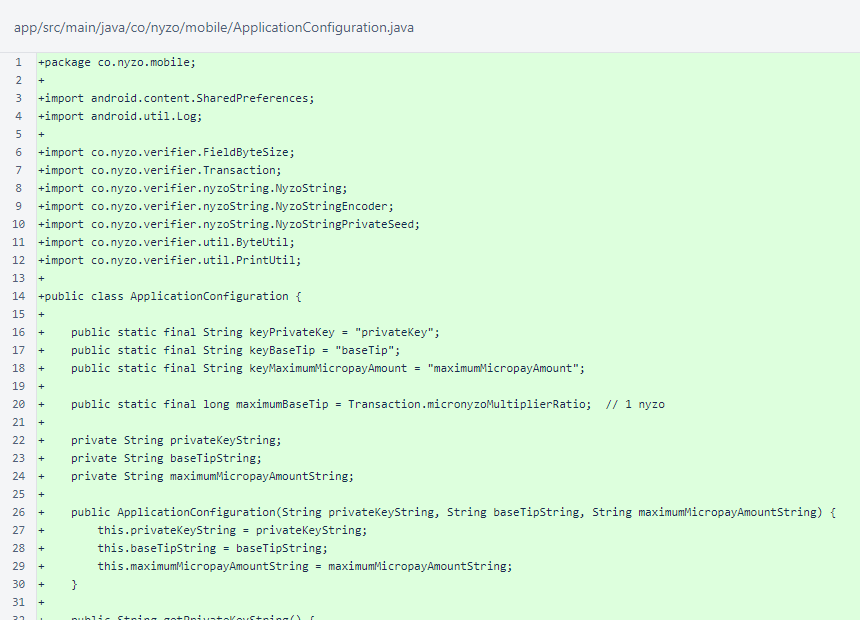
The ApplicationConfiguration class is used to encapsulate, store, and retrieve the private key, base tip, and maximum Micropay amount required to use the app.
All three fields are stored as strings to allow them to be consistently presented in the manner that the user prefers. Accessors to these string values are provided, as are accessors to the respective values converted to the required data types.
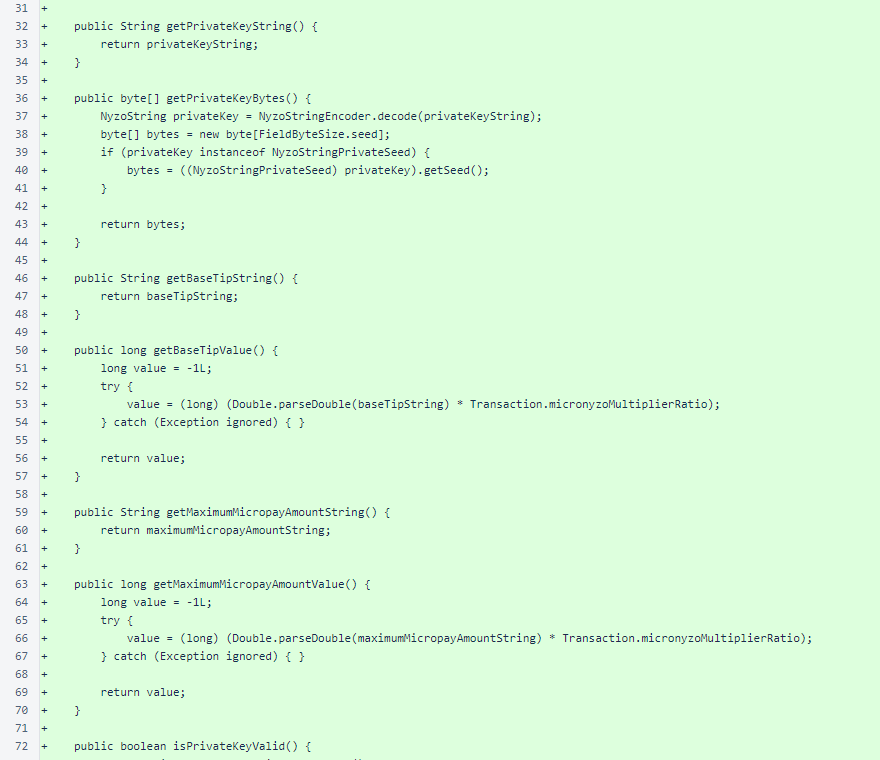
Separate methods are provided for validating each of the fields, and a combined method validates all three fields to determine whether the overall application configuration is valid.

One method is provided to load the application configuration from SharedPreferences, and another method is provided to persist the configuration to SharedPreferences.

The Icon class encapsulates a Path, Paint, and a "fillRatio" for rendering an icon. The "fillRatio" is a scaling factor, with smaller values scaling the icon to fill less of the interface element in which it is rendered.

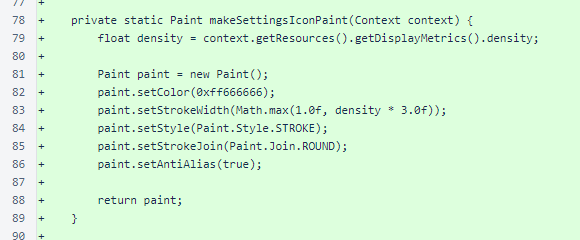
A method is provided to make an icon for the Settings button, and a method builds a Path for that icon. This path is a gear with seven teeth.

The Paint for the Settings icon specifies a narrow gray stroke with a round join.
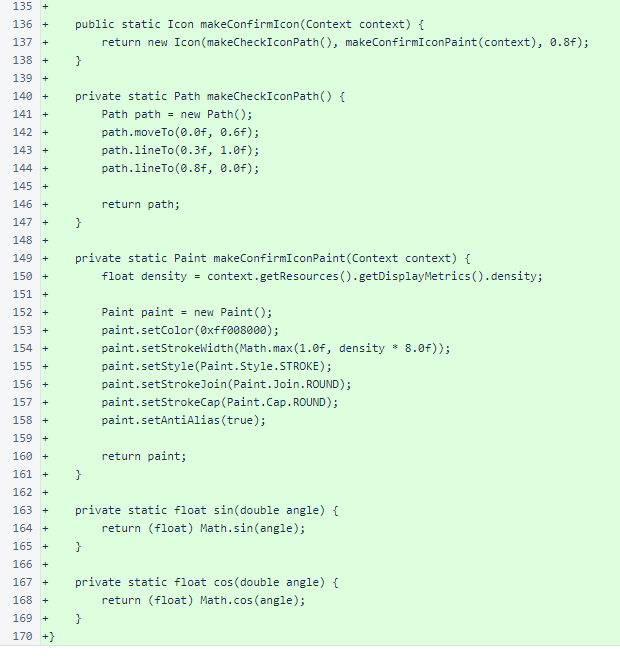
The Cancel and Close icons share a path in the shape of an "X." The Cancel icon specifies a red Paint, and the Close icon specifies a gray Paint.

The Confirm icon is a green check mark. The sin() and cos() helper methods call their respective methods in the Math class and cast their results to float.
The InterfaceState enumeration structures the three main states of the app: WaitingForInput, SendingTransaction, and SentTransaction. While the user has the app open, the state will almost always be WaitingForInput.

The MainActivity is the app entry point, specified in AndroidManifest.xml. A static reference to the newest instance of MainActivity is stored for convenience.
Lists of messages, warnings, and errors, along with a boolean variable to store success or failure, are kept to represent the result of sending a transaction.
The micropayConfiguration and settingsViewVisible are stored in static, not instance, variables. This allows them to exist for the duration of the app, even if a new instance of the activity is created. A new activity is created each time the screen is rotated, so this is necessary for an acceptable user experience.

The MainActivity.onCreate() method creates the mainView, sets listeners for its buttons, initializes state variables, and performs an initial interface configuration.

The MainActivity.configureWithIntent() method extracts the micropayConfiguration (from the nyzo://micropay URL) from the Intent and configures the mainView.
The MainActivity.sendTransaction() method starts a new thread to send a transaction. The MainActivity.sendTransactionThread() method sends a transaction, if necessary, creates a supplemental transaction, and redirects back to the page with both the transaction and the supplemental transaction.

All transactions are stored so they can be re-sent without sending a new transaction and paying for content again. The MainActivity.clearTransaction() method clears an existing transaction so a new transaction can be created. This is helpful if an existing transaction is not working properly for authorizing content.
The MainActivity.retry() method resets the interface after failure.
The MainActivity.createTransactionAndSendToClient() method creates a transaction for the amount specified in a Micropay configuration, sends it to the client specified in the configuration, and stores the response.
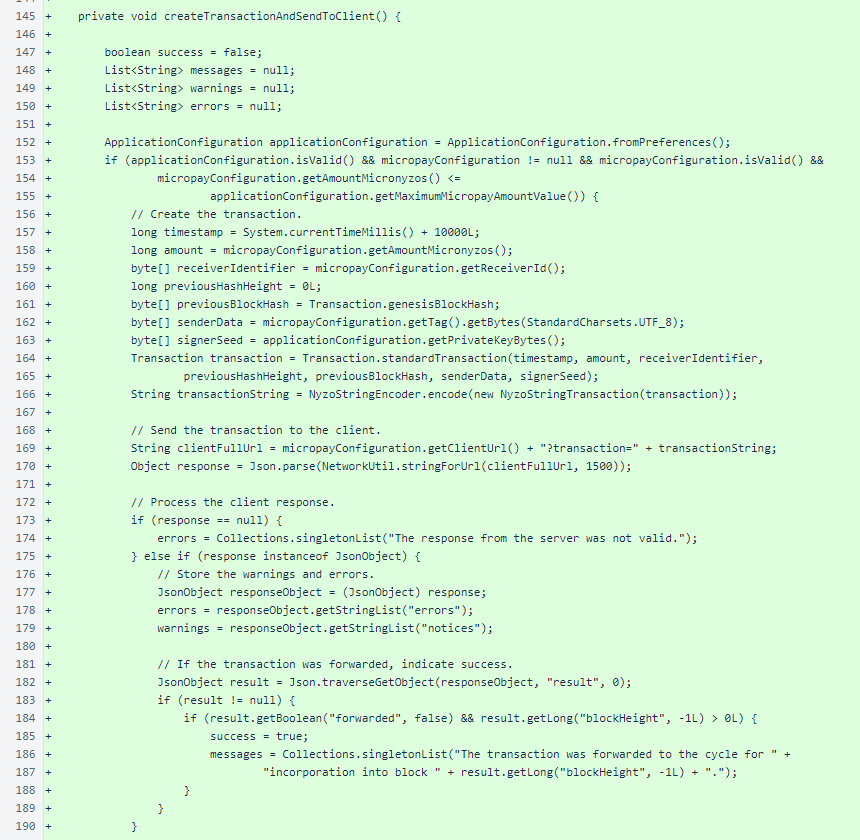
After ensuring that appropriate feedback is available, the MainActivity.createTransactionAndSendToClient() method dispatches an update to the user-interface thread to present the results to the user.
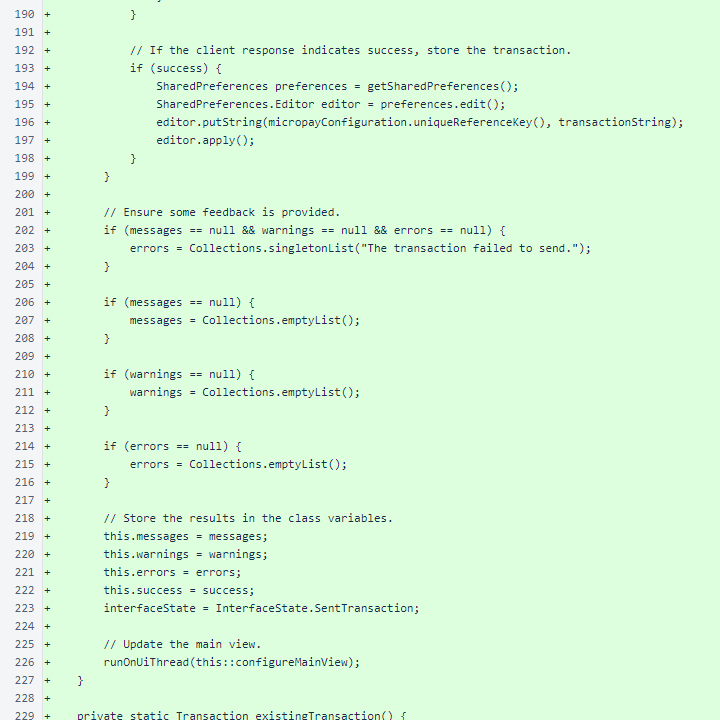
The MainActivity.existingTransaction() method retrieves a stored transaction from the app's SharedPreferences.
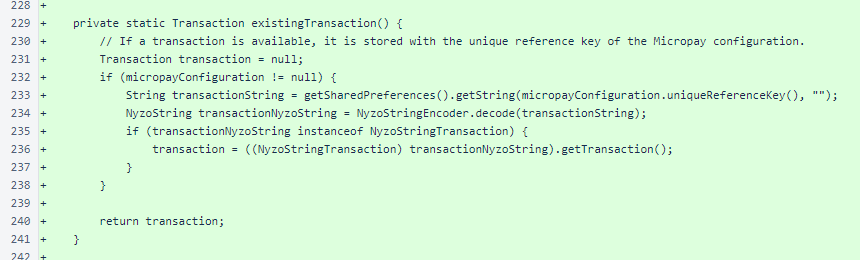
The MainActivity.parseMicropayConfiguration() method extracts a MicropayConfiguration from a Micropay URL. The MainActivity.mapForString() method returns URL query string key/value pairs as a Map.
An accessor and mutator are provided for visibility of the settingsView. A static convenience method hides the soft keyboard, and another convenience method provides a reference to the app's SharedPreferences.
A helper method creates a new µ0 supplemental transaction that parallels a provided transaction.
The MainView encapsulates the PaymentView and the SettingsView. It provides passthrough OnClickListeners to bridge from the PaymentView to the MainActivity.

In the MainView constructor, the paymentView and settingsView are created. Appropriate OnClickListeners are set.

The MainView.onLayout() method places both the paymentView and settingsView full-size within the MainView. A translation along the y axis controls whether the settingsView is visible or is off screen.
Mutators store OnClickListeners. The MainView.showSettingsView() and MainView.hideSettingsView() methods animate the settingsView on and off the screen.
The MainView.configure() method passes through to the PaymentView.configure() method.
The MapUtil class, as the comment explains, is used to overcome a deficiency in the Android Java libraries prior to API level 24.
The MicropayConfiguration class encapsulates all the information necessary for making a Nyzo Micropay payment. The callbackUrl field is new to this embodiment of Micropay; it was not necessary for the browser plugin.
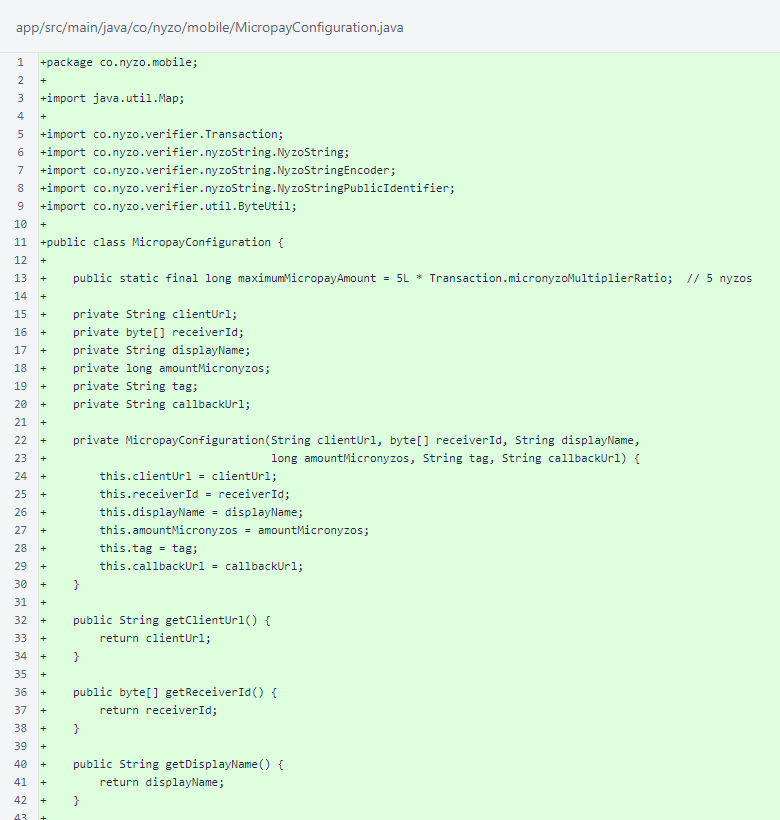
Accessors are provided for all fields, and a method performs a basic validity check. The MicropayConfiguration.uniqueReferenceKey() method provides a unique key for storing transactions for reuse. The MicropayConfiguration.fromMap() method creates a MicropayConfiguration object from a Map containing key/value pairs for all fields.
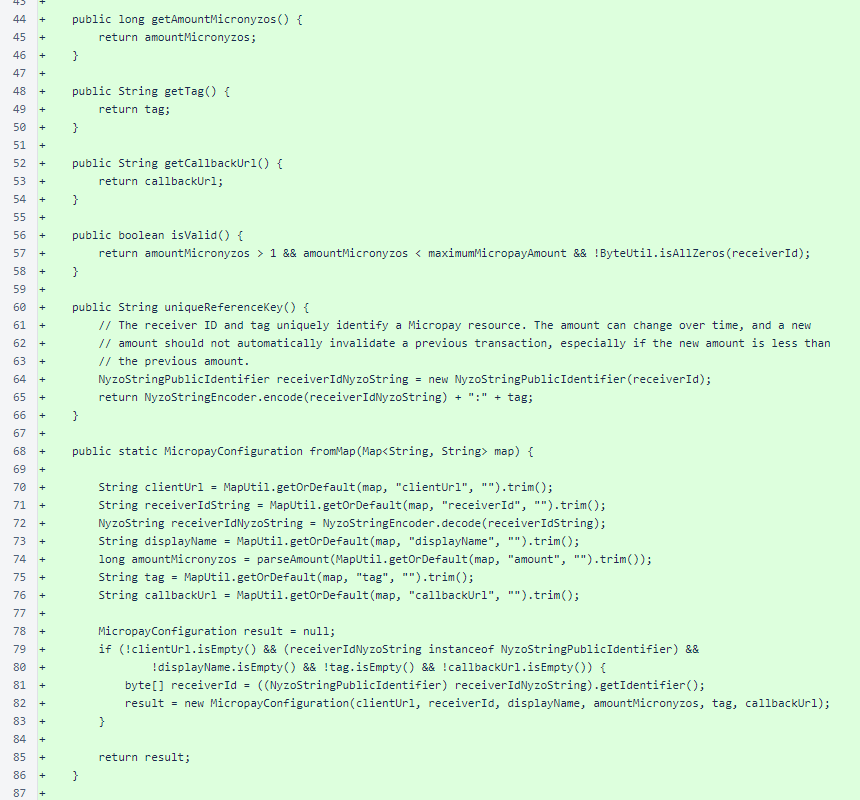
The parseAmount() helper method parses a decmial value in nyzos to a long micronyzo value.
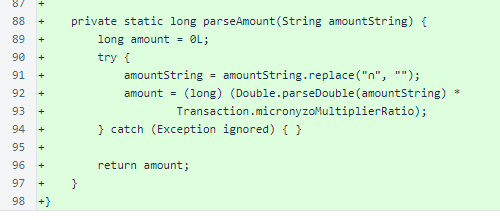
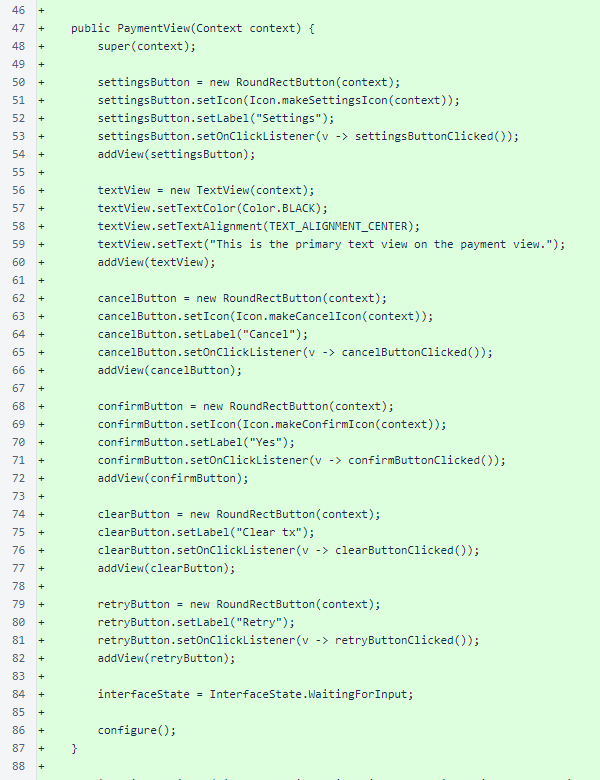
The PaymentView class provides the main interface of the app. All necessary state is stored in member variables, and the interface configures itself based on this state.
The PaymentView constructor makes all of the buttons for the view, sets the OnClickListeners and an initial interface state, and performs an initial configuration.
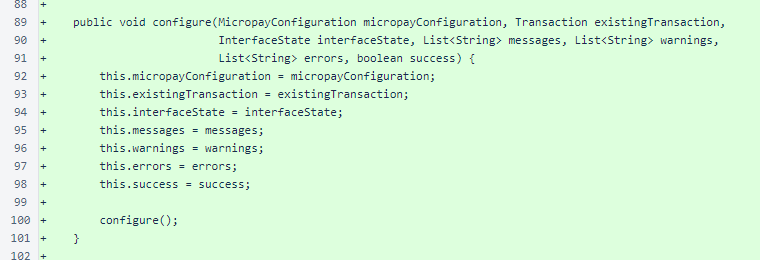
The parameterized PaymentView.configure() overload stores the arguments as internal state and calls the no-argument overload of the method.
The no-argument PaymentView.configure() overload presents a message to the user based on the current state. It also presents the appropriate buttons for the user to act upon that state.
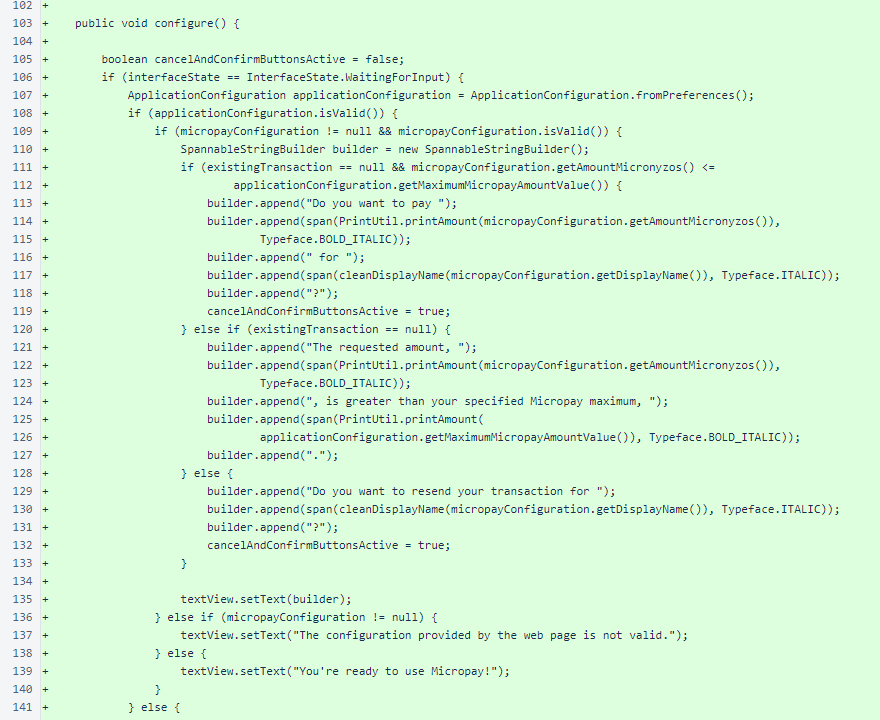
In the PaymentView.configure() method, a SpannableStringBuilder is used to style spans of text.

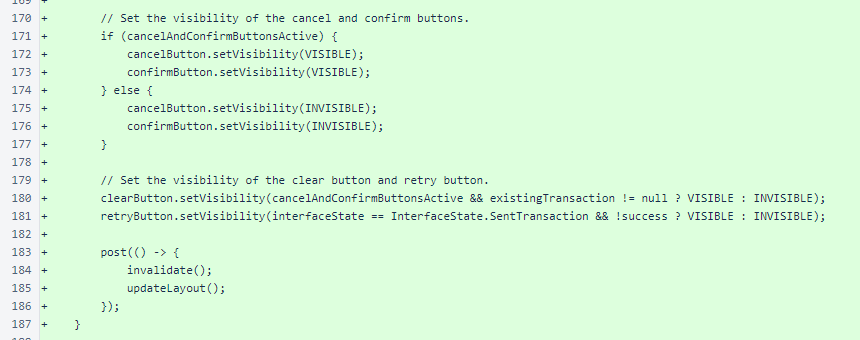
Unused buttons are set to View.INVISIBLE. Both invalidate() (requesting a redraw) and updateLayout() are called at the end of the method, posted to the queue for the UI thread.
The PaymentView.span() convenience method creates a SpannableString with a StyleSpan with the specified style. The PaymentView.cleanDisplayName() method attempts to remove potentially misleading elements from the name that is presented for a potential payment, also trimming the name to a reasonable length. The PaymentView.onSizeChanged() method updates the text size of the label, and the PaymentView.onLayout() method updates the layout.
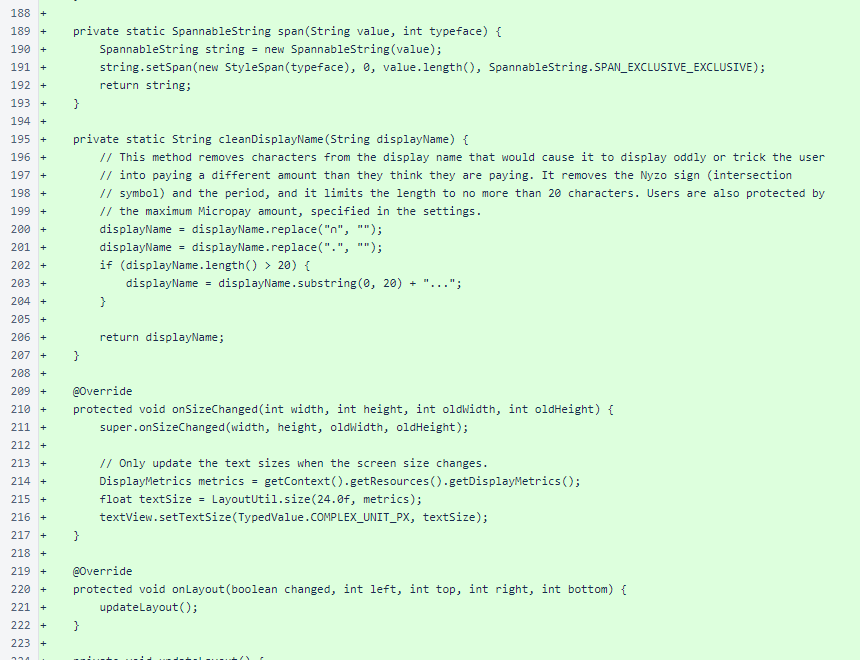
The PaymentView.updateLayout() method arranges the child views of the payment view. Instead of using LayoutManagers, all interfaces in this app extend ViewGroup and perform layouts procedurally. This is an unconventional approach in Android development.
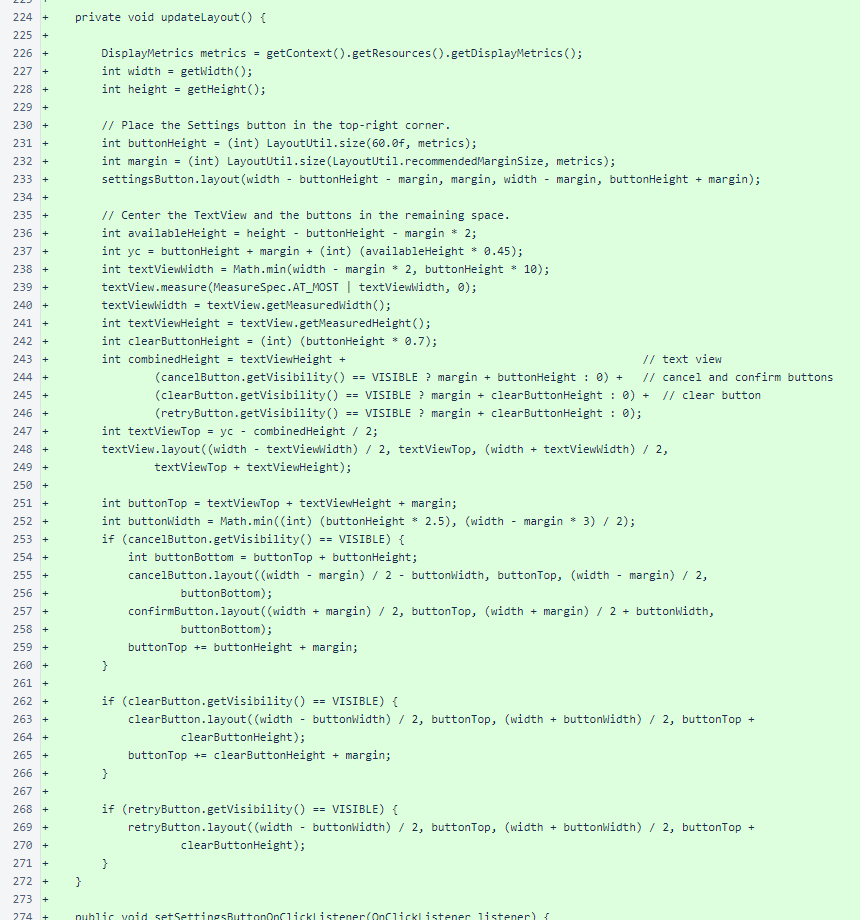
Mutators are provided for all OnClickListeners.
When buttons are activated, the corresponding OnClickListeners are called.

The RoundRectButton class provides a button with a rounded border, an icon, and a text label.
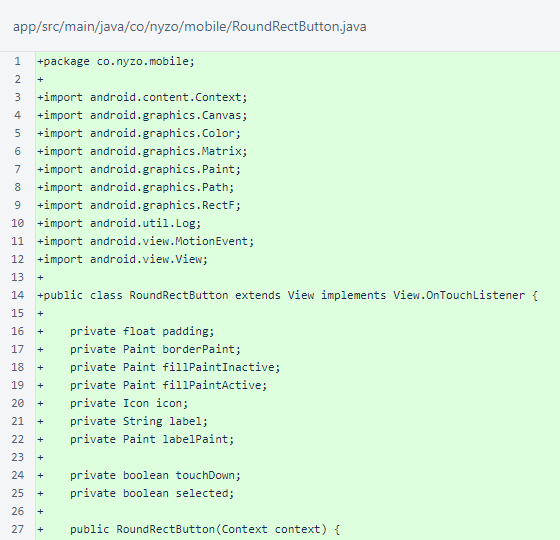
The RoundRectButton constructor creates Paint objects for the border, fill, and text label. It also sets the listener for touch events.

A custom onTouch() is implemented so that the button can be darkened when pressed. In order to continue receiving events after the initial touch, the touch must be consumed. When the touch is consumed, responsibility for activating a click is assumed. The method calls the callOnClick() method to fulfill this responsibility.

The RoundRectButton.performClick() method was implemented for logging during testing. This implementation will be removed in a later version. The RoundRectButton.setSelected() method stores the selection state and requests a redraw of the button.

The RoundRectButton.draw() method draws the custom button. A background, rounded border, label (optional), and icon (also optional) are drawn to appropriate scale.

Mutators are provided for the icon and label. A convenience method provides a scaled version of the icon path to fit the button.

The SettingsView interface allows the user to specify the private key, base tip amount, and maximum Micropay amount. The privateKeyEditTextPaint is used as a reference to assist in scaling the private key text field to ensure it fits in the available space.
The SettingsView constructor creates all the user interface elements and the privateKeyEditTextPaint.

The SettingsView constructor continues with user interface elements for the notices and the close button.

The SettingsView.onSizeChanged() method updates font sizes and field padding. It also invokes updateTextFieldProperties(), which sets the x scaling of the private key edit text.

SettingsView.onLayout() arranges the subviews of the SettingsView.
The notices are positioned at the bottom of the view, and updateTextFieldProperties() is invoked to ensure the private key is scaled properly for the new field size.
A mutator is provided for the closeButtonOnClickListener. When the close button is clicked, focus is removed from all text fields, the keyboard is hidden, and the closeButtonOnClickListener.onClick() method is invoked.
The SettingsView.beforeTextChanged() and SettingsView.onTextChanged() methods are required by the TextWatcher interface but not needed by this class. The SettingsView.afterTextChanged() method saves the field values and updates the text field properties, which sets both the x scaling of the private key field and updates the field colors to provide feedback about configuration validity.
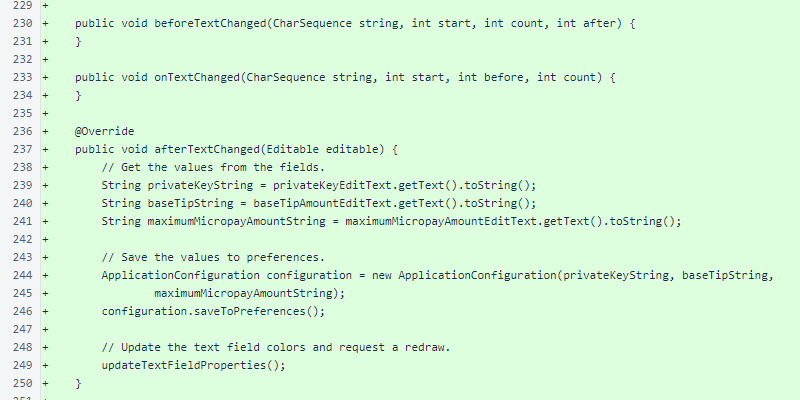
The SettingsView.updateTextFieldProperties() method sets the background color of the edit texts: red for invalid and green for valid. It also sets the x scale of the private key edit text to ensure that the entire key is visible in the field.

The FieldByteSize class is identical to the corresponding class in the verifier source, version 606.
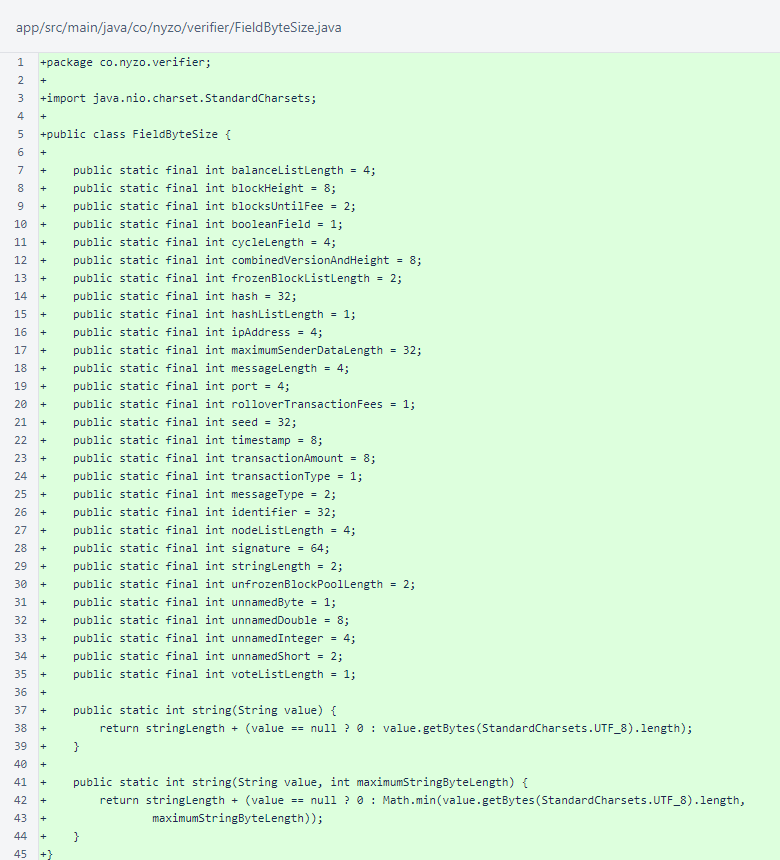
The Message class borrows a single static method, getByteArray() from the verifier source.
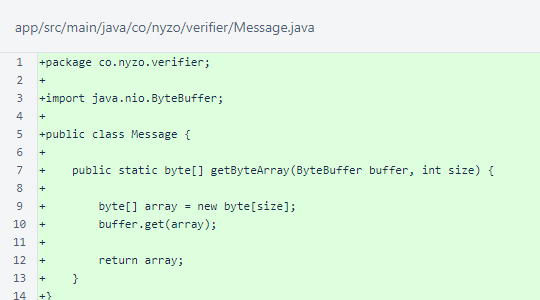
The MessageObject interface is identical to the corresponding class in the verifier source, version 606.
The SignatureState enumeration is identical to the corresponding class in the verifier source, version 606.
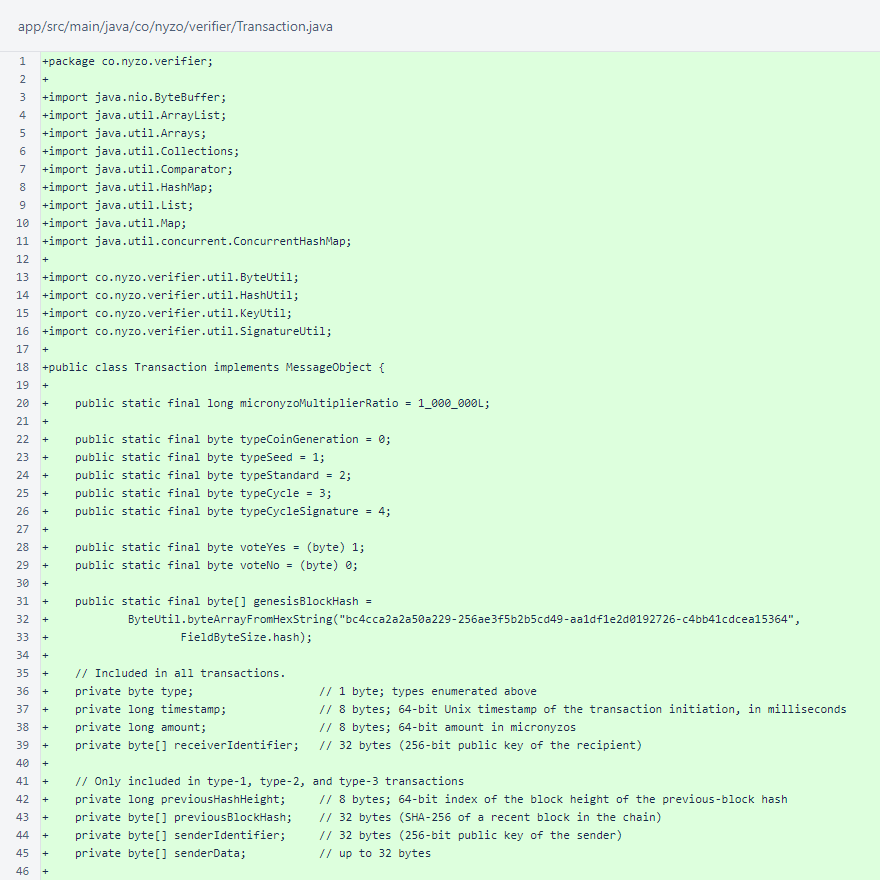
The Transaction class borrows heavily from the corresponding class in the verifier source. Some unused constants have been removed, and the GenesisBlockHash was added.
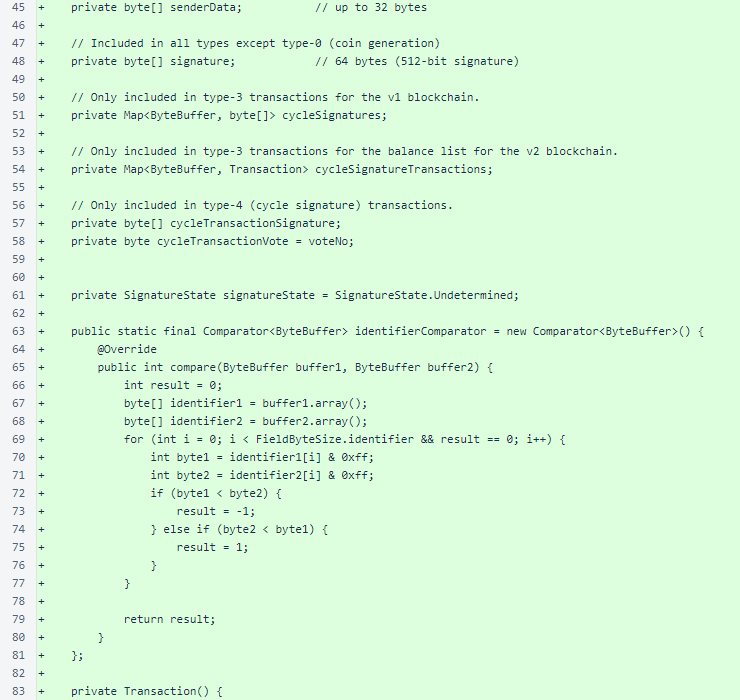
The Transaction private instance fields and identifierComparator are identical to those found in the verifier's version of the class.
The Transaction accessors are identical to those found in the verifier's version of the class. Some methods for handling cycle signature transactions were removed.

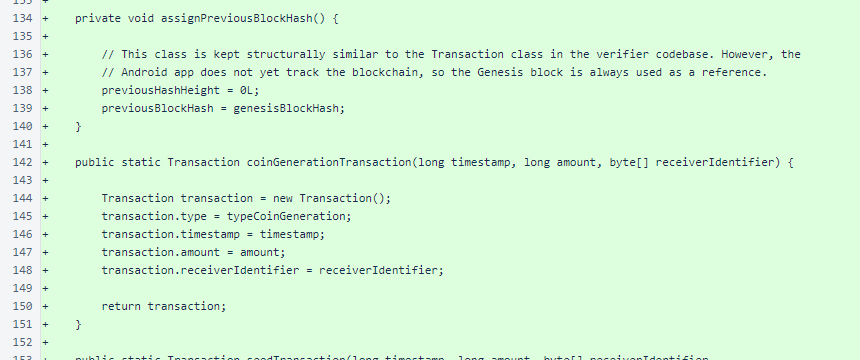
The Transaction.assignPreviousBlockHash() method was changed to always use the genesisBlockHash, as explained in the comment.
The Transaction.coinGenerationTransaction() method is identical to the corresponding method in the verifier's version of the class.
The Transaction.seedTransaction() methods are identical to the corresponding methods in the verifier's version of the class.

The Transaction.standardTransaction() methods are identical to the corresponding methods in the verifier's version of the class.
The first two overloads of Transaction.cycleTransaction() are identical to the corresponding methods in the verifier's version of the class.
The third overload of Transaction.cycleTransaction() is identical to the corresponding method in the verifier's version of the class, with the exception of the line assigning the previousBlockHash. This is now assigned the genesisBlockHash.
The final two overloads of Transaction.cycleTransaction() are identical to the corresponding methods in the verifier's version of the class.

The Transaction.getFee() and Transaction.getByteSize() overload with no arguments are identical to the corresponding methods in the verifier's version of the class.
The primary Transaction.getByteSize() overload is also identical to the corresponding method in the verifier's version of the class.

The Transaction.getBytes() methods are identical to the corresponding methods in the verifier's version of the class, with the minor exception of the sorting at lines 431 and 440. These calls were changed due to a deficiency in the Android library.
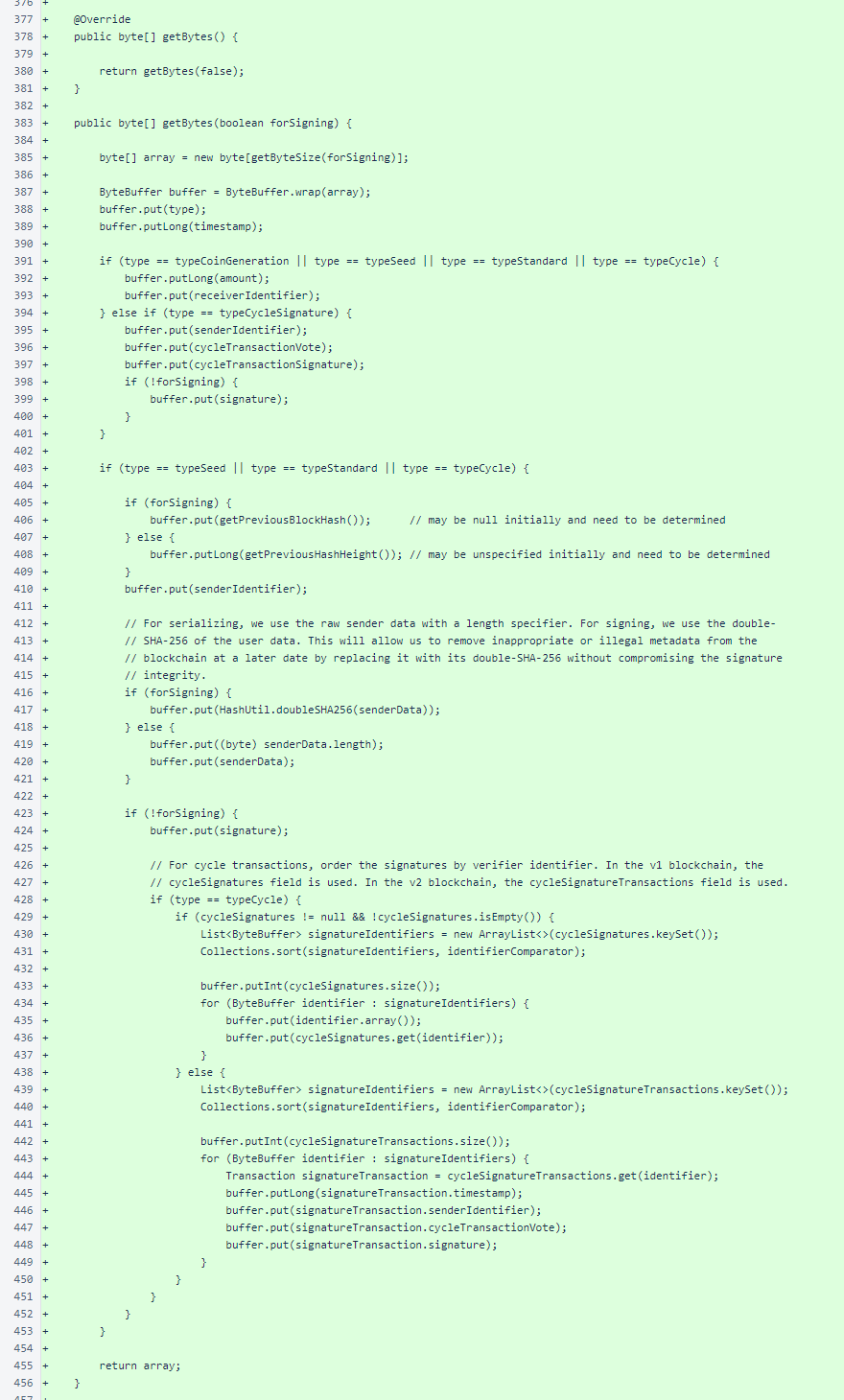
The Transaction.fromByteBuffer() methods are also the same as the equivalent methods in the verifier source, with the exception of the assignment of previousBlockHash at line 483. As is explained in the comments, the app currently supports only transactions referenced to the Genesis block.
Several methods from the end of the Nyzo verifier source file have been omitted from the Android version of the class. These will be added in future versions if needed.
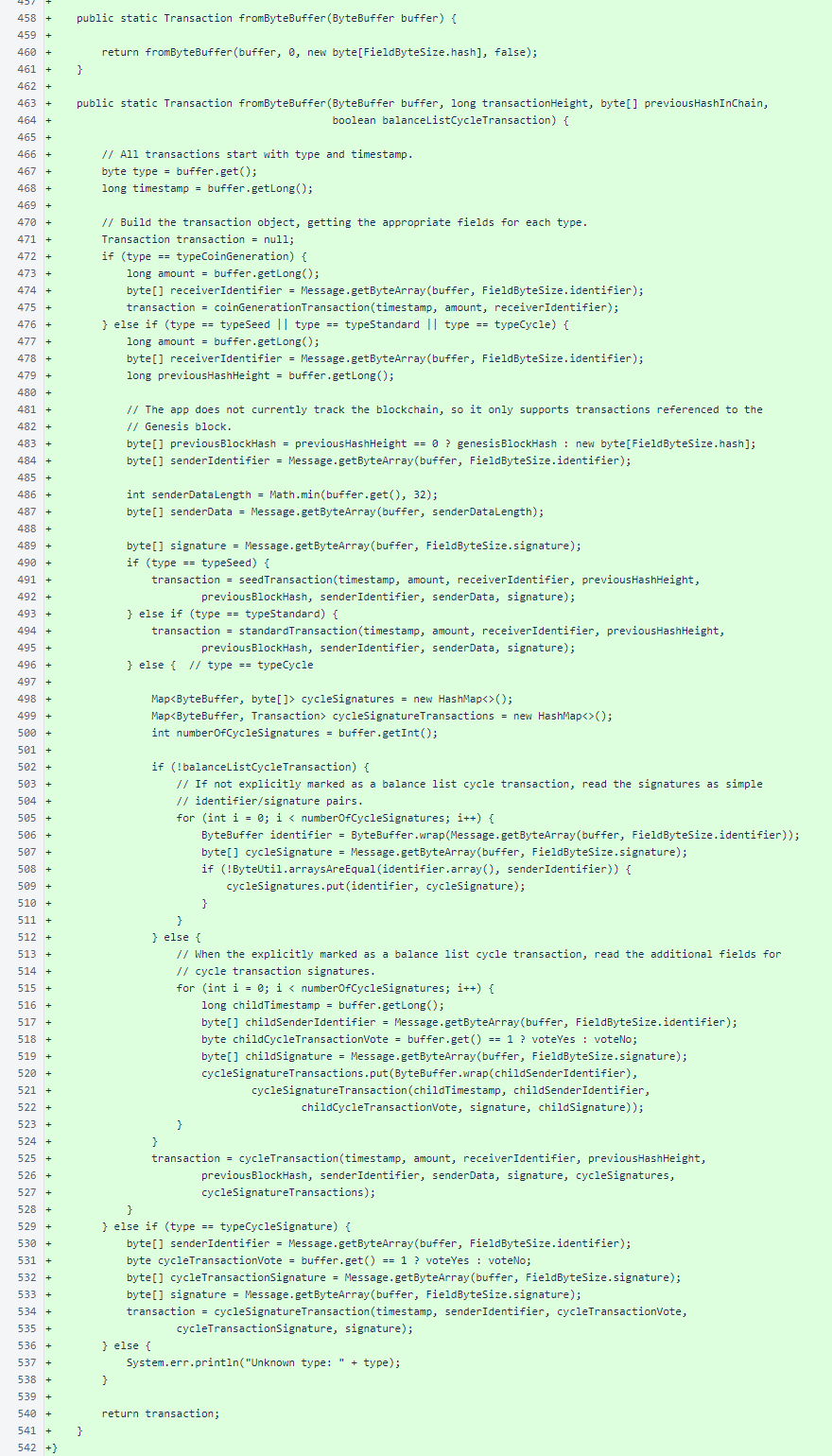
The Json class is largely identical to the class in the verifier source, with the exception of maximumJsonStringLength at line 12 and some added methods. In the verifier, the maximumJsonStringLength field is private and final. It was changed for flexibility in testing, and it will be aligned with the verifier in a future version.
This section of the Json class is unchanged from the verifier source.

This section of the Json class is unchanged from the verifier source.

This section of the Json class is unchanged from the verifier source.

This section of the Json class is unchanged from the verifier source.
This section of the Json class is unchanged from the verifier source.

The Json.traverse() method, a new method in the Android version of the class, is used as shorthand to extract an object from a JSON hierarchy. The Json.traverseGetArray() method returns the result as a JsonArray, and the Json.traverseGetObject() method returns the result as a JsonObject.

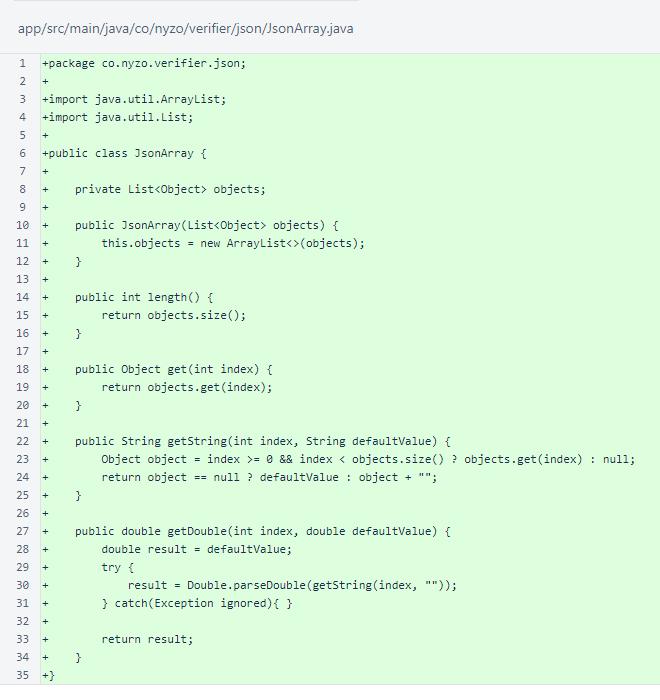
The JsonArray class is unchanged from the verifier version.
The JsonObject class begins exactly the same as the verifier version.
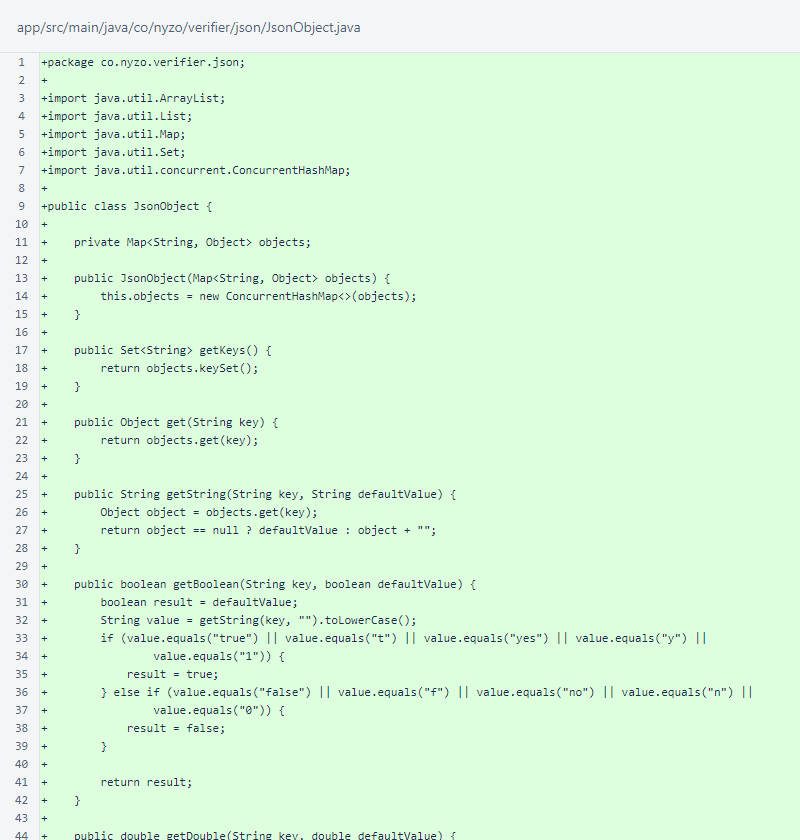
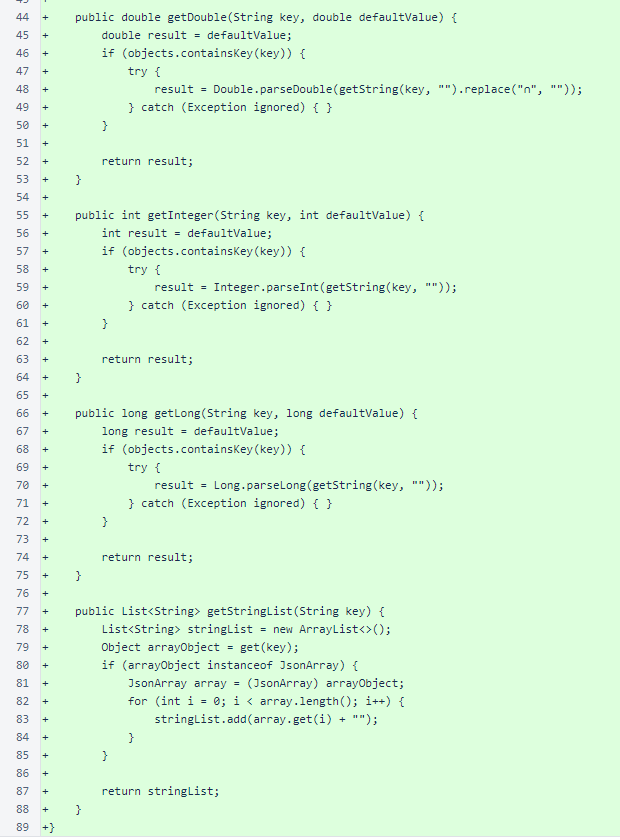
The JsonObject class concludes with three new methods: getInteger(), getLong(), and getStringList(). These methods will be added to a future version of the verifier.
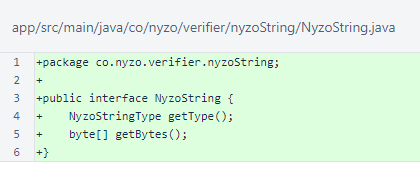
The NyzoString interface is identical to the verifier version.
The beginning of the NyzoStringEncoder class is identical to the verifier version.
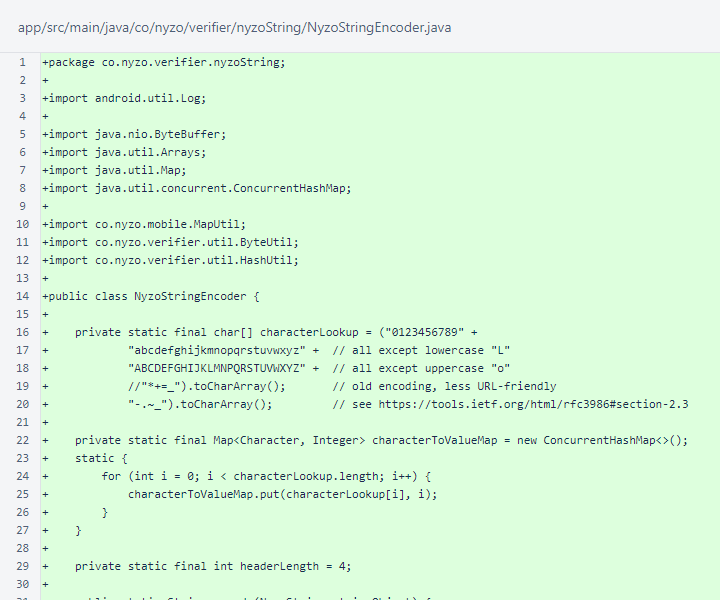
In NyzoStringEncoder.encode(), at line 49, fast iteration is used. The verifier version of this method iterates with an index. The verifier will also be updated with this change.
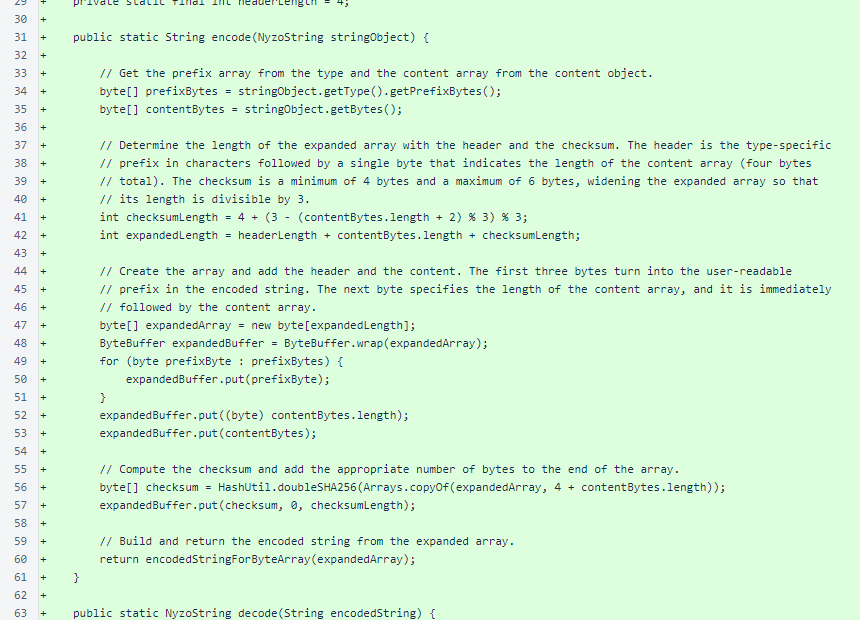
In NyzoStringEncoder.decode(), at line 73, a different replacement for lowercase "L" (l) is used. Instead of a numerical "1" substitution, uppercase "i" (I) is used, as this is a more common mistake with most fonts. In these notes, the sans-serif font used by most browsers will likely illustrate this well.

Building of the result object at the end of NyzoStringEncoder.decode() is identical between the Android and verifier versions.
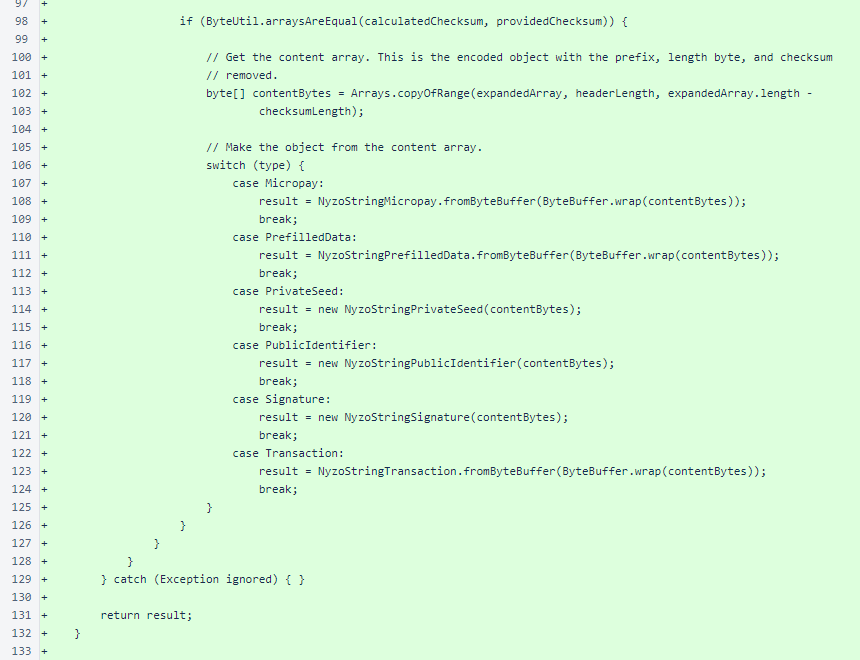
In NyzoStringEncoder.byteArrayForEncodedString(), at lines 143 and 144, MapUtil.getOrDefault() is used because Map.getOrDefault() is unavailable on some versions of Android that the app currently supports.
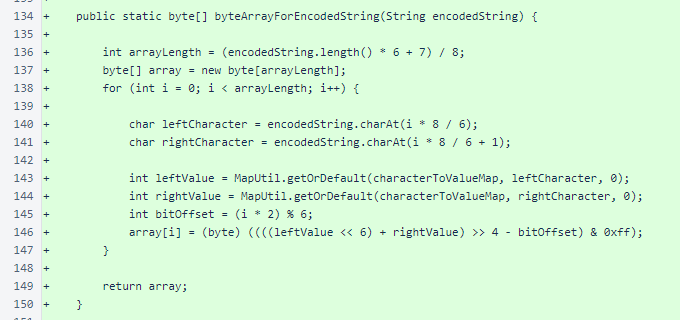
NyzoStringEncoder.encodedStringForByteArray() is identical between the Android and verifier versions.

The NyzoStringMicropay class is unchanged from the verifier version.
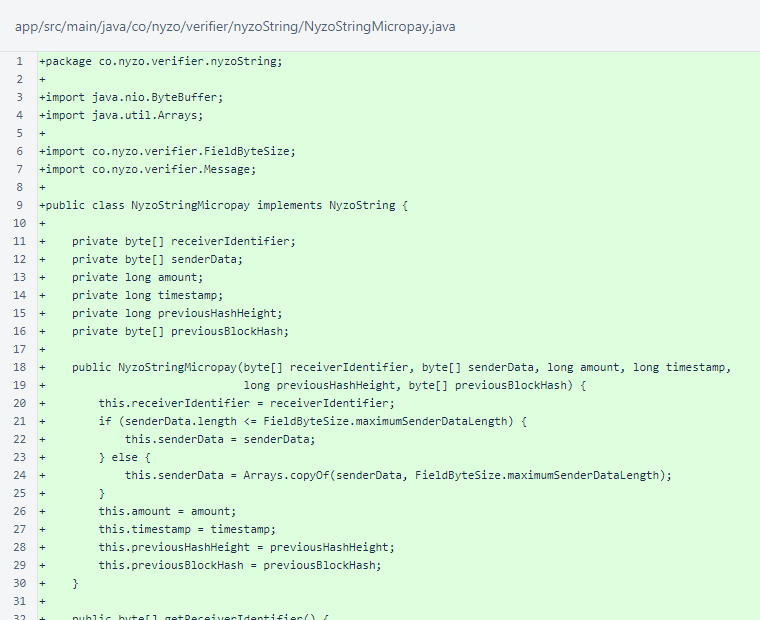
Continued: the NyzoStringMicropay class is unchanged from the verifier version.

Continued: the NyzoStringMicropay class is unchanged from the verifier version.
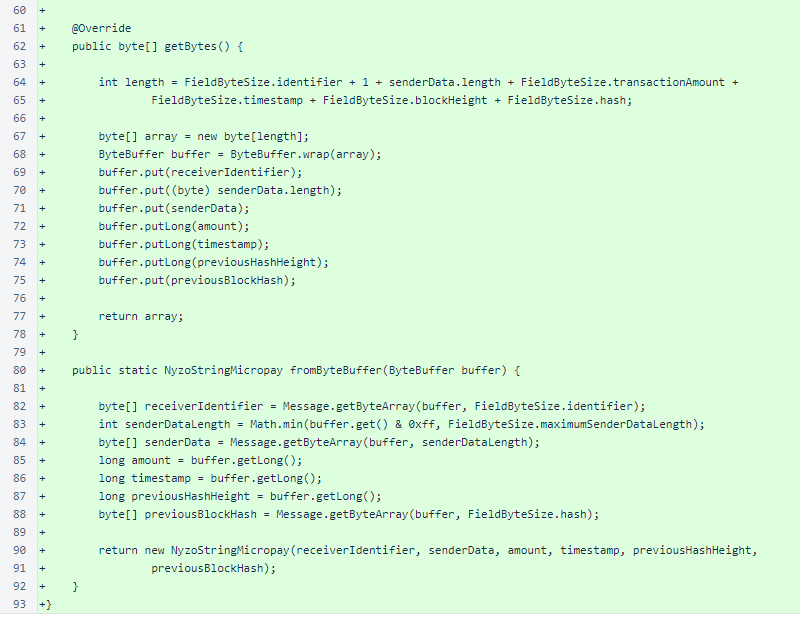
The NyzoStringPrefilledData class is unchanged from the verifier version.

The NyzoStringPrivateSeed class is unchanged from the verifier version.

The NyzoStringPublicIdentifier class is unchanged from the verifier version.

The NyzoStringSignature class is unchanged from the verifier version.

The NyzoStringTransaction class is unchanged from the verifier version.

The NyzoStringType enumeration is unchanged from the verifier version.

The ByteUtil class is a trimmed-down form of the verifier version. The toArray(), dataSegment(), signatureSegment(), arrayAsStringNoDashes() overload that accepts a long argument, and arrayAsStringWithDashesExtraWrap() methods were omitted from the Android version.

Continued: the ByteUtil class is a trimmed-down form of the verifier version.
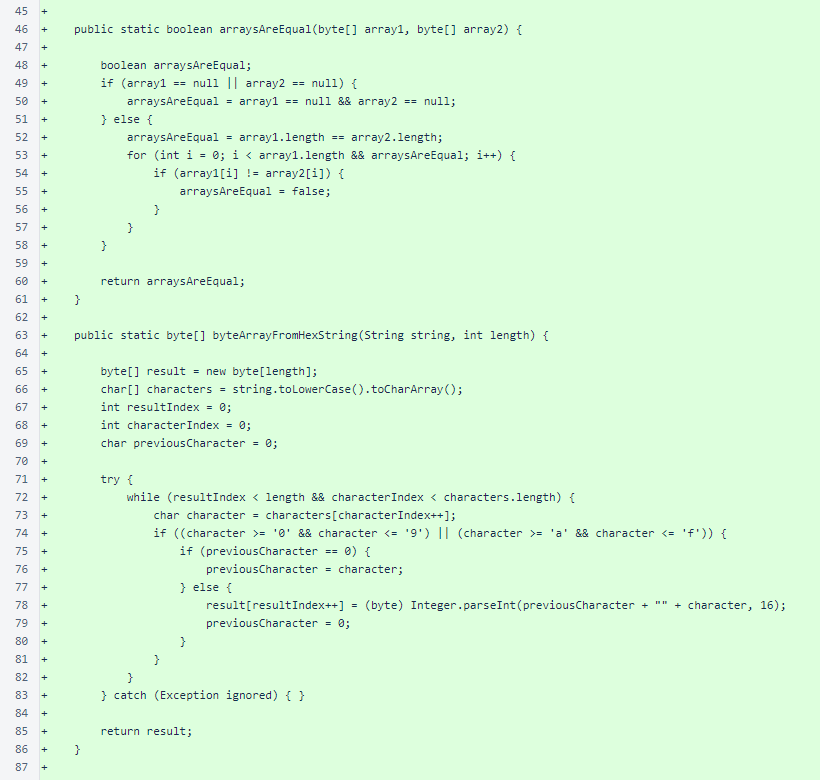
Continued: the ByteUtil class is a trimmed-down form of the verifier version.
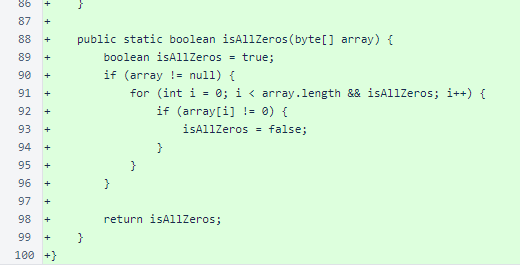
The HashUtil class is almost identical to the verifier version, omitting only the main() method test script.

Continued: the HashUtil class is almost identical to the verifier version, omitting only the main() method test script.

Continued: the HashUtil class is almost identical to the verifier version, omitting only the main() method test script.

The KeyUtil class is a trimmed down form of the verifier version, omitting the main() method test script and the generateSeed() method.
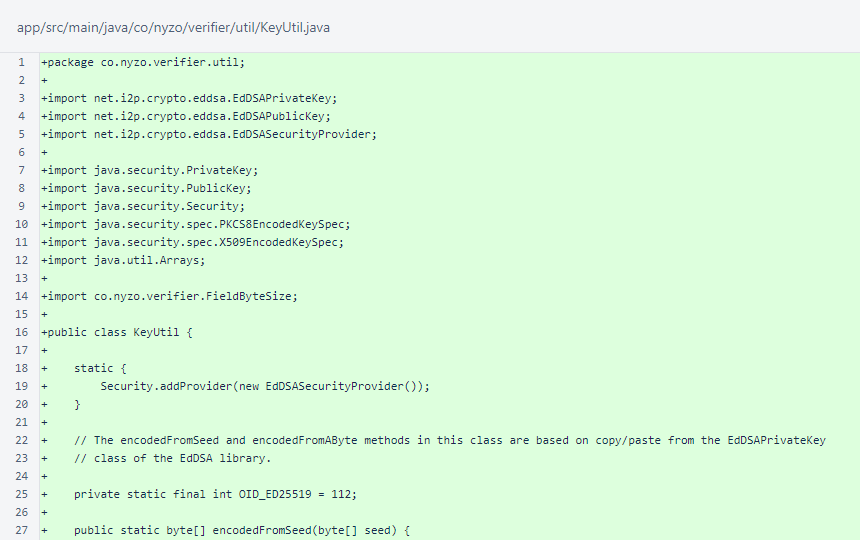
Continued: the KeyUtil class is a trimmed down form of the verifier version, omitting the main() method test script and the generateSeed() method.
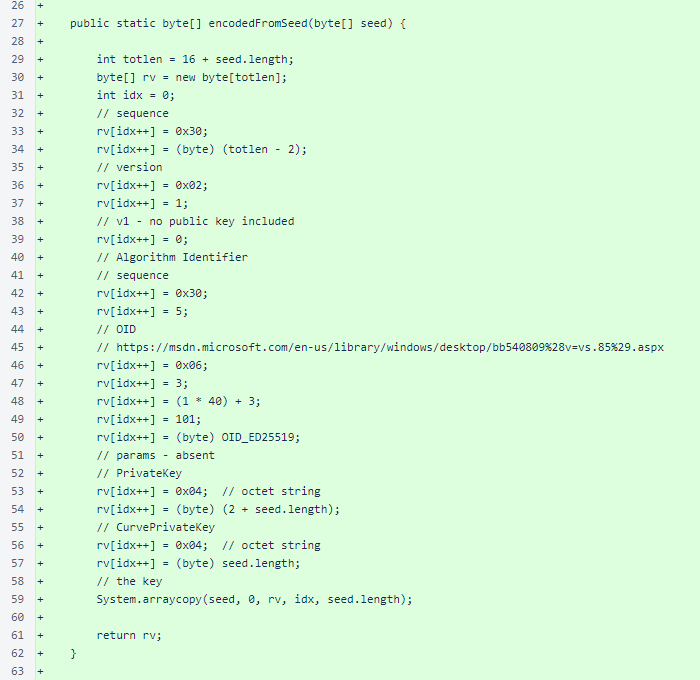
Continued: the KeyUtil class is a trimmed down form of the verifier version, omitting the main() method test script and the generateSeed() method.
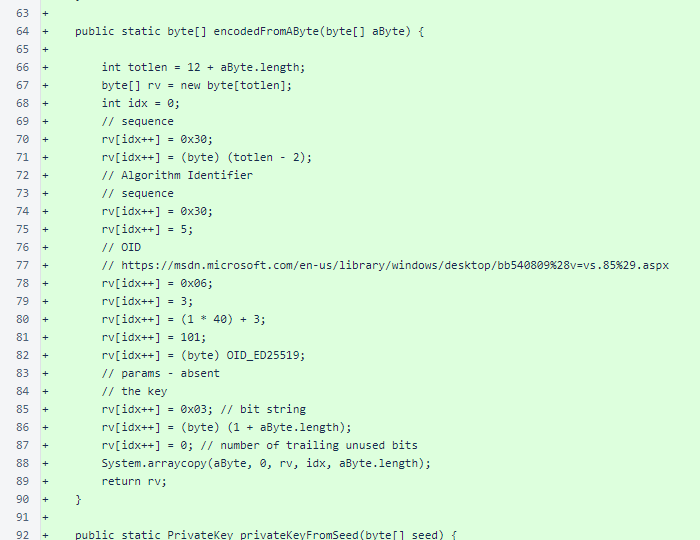
Continued: the KeyUtil class is a trimmed down form of the verifier version, omitting the main() method test script and the generateSeed() method.
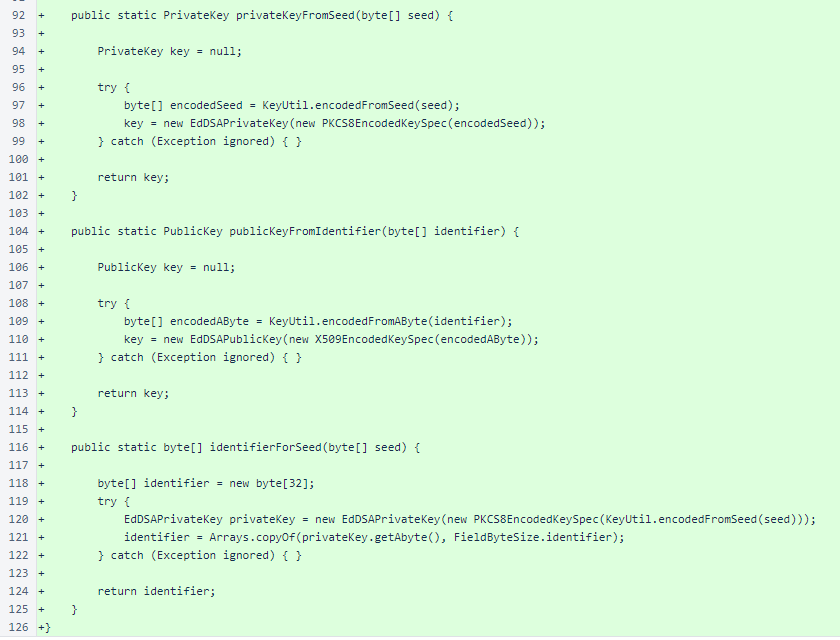
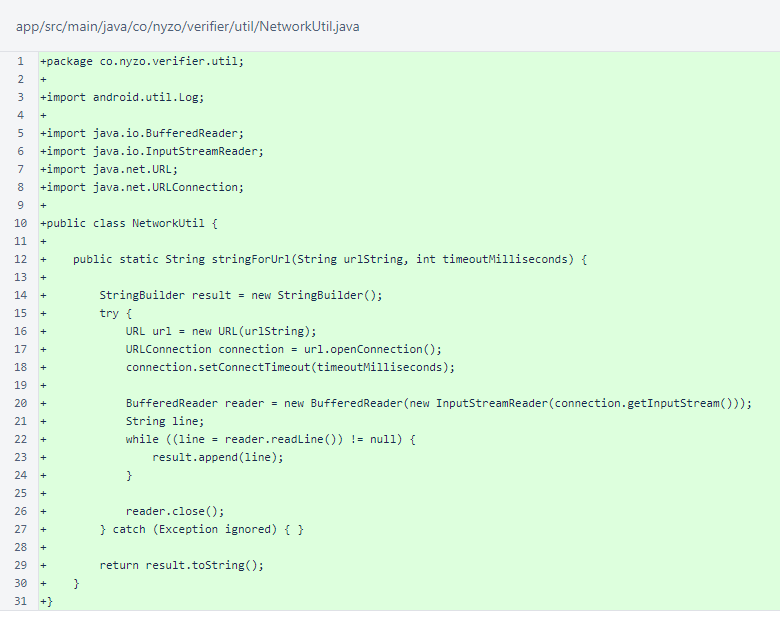
The NetworkUtil class is identical to the verifier version.
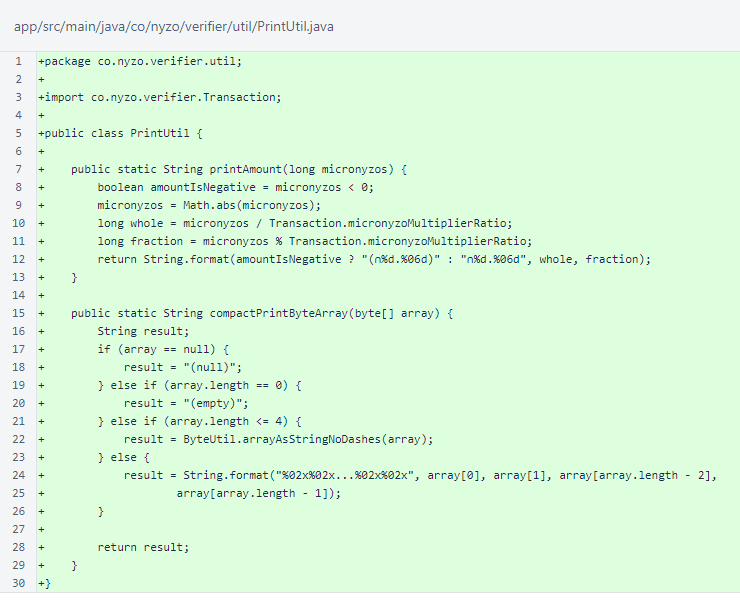
The PrintUtil class is a significantly trimmed down form of the verifier version, containing only the printAmount() and compactPrintByteArray() methods.
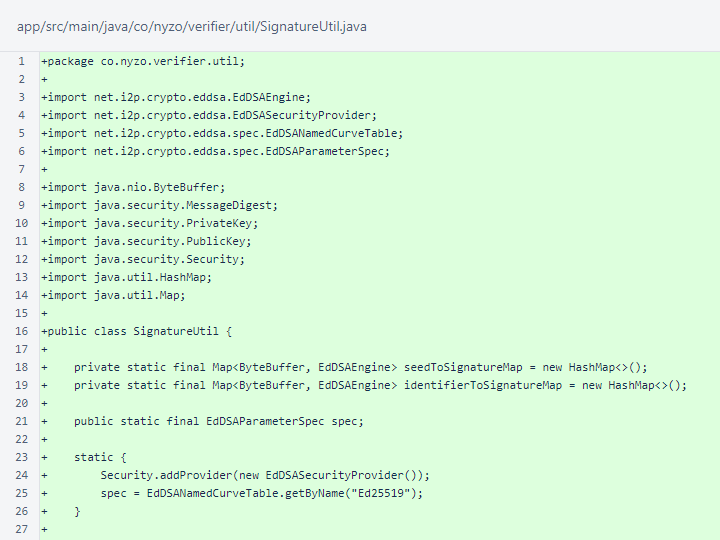
The SignatureUtil class is identical to the verifier version.
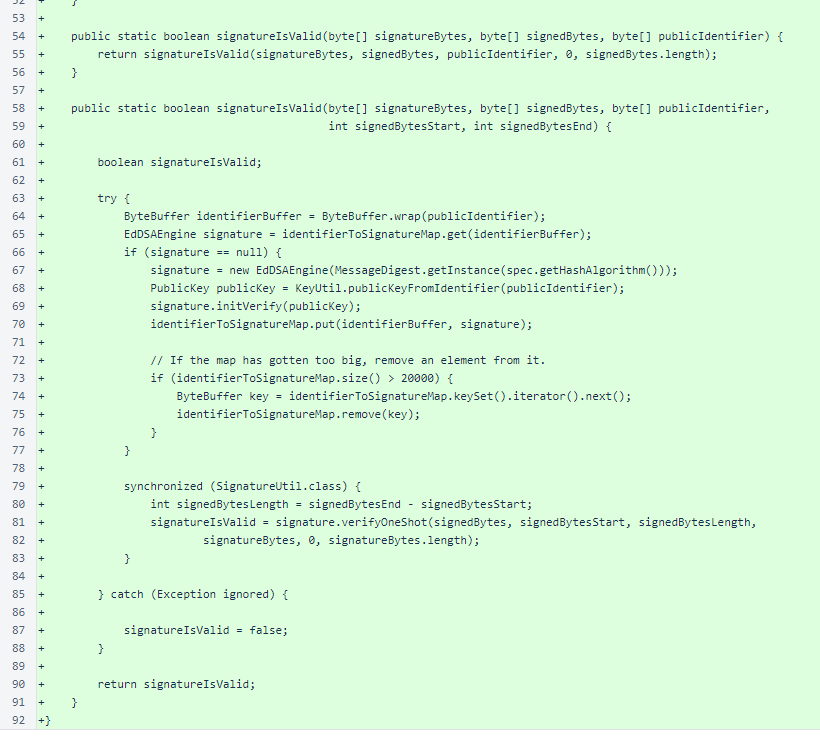
Continued: the SignatureUtil class is identical to the verifier version.

Continued: the SignatureUtil class is identical to the verifier version.
The WebUtil class is a trimmed down form of the verifier version, containing only the applyPercentEncoding() and removePercentEncoding() methods, along with support for those methods.
As in some other classes, the MapUtil.getOrDefault() method is used in place of the Map.getOrDefault() method. This occurs at line 42 in WebUtil.applyPercentEncoding() and line 64 in WebUtil.removePercentEncoding.
